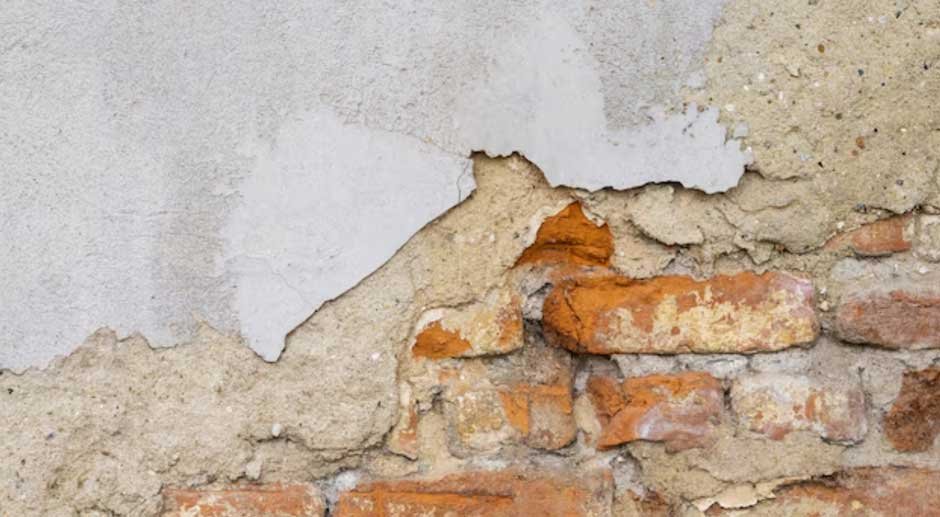
A strong foundation is the backbone of any structure, be it a residential home or a towering skyscraper. When the foundation weakens or suffers damage, the consequences can be severe, ranging from structural instability to costly repairs and even potential safety hazards.
In this article, we’ll explore five preventative measures you can take to protect your foundation and safeguard your property from the headaches and expenses of foundation damage.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Ensure proper drainage and grading around your home’s foundation to direct water away from the structure.
- Maintain a safe distance between trees/vegetation and the foundation to prevent root damage and soil shifting.
- Compact the soil properly during construction and monitor for signs of settlement or erosion.
- Implement waterproofing methods and control moisture levels through ventilation and insulation.
1. Proper Drainage and Grading
Water is one of the biggest enemies of a solid foundation. Excess moisture can seep into the soil, causing it to expand and shift, putting immense pressure on the foundation walls. That’s why directing water away from your home’s foundation is crucial.
Start by ensuring proper grading around the foundation. The ground should slope away from the structure, allowing water to drain naturally. If you notice any low spots or depressions, they need to be filled to prevent water from pooling.
Installing drainage systems like French drains or catch basins can also be a game-changer. These systems collect and divert water away from the foundation, minimizing the risk of moisture buildup. And let’s not forget about those downspouts and gutters. Extend them several feet away from the foundation to keep water from saturating the soil nearby.
2. Tree and Vegetation Management
While trees and shrubs add beauty and curb appeal to your property, their roots can wreak havoc on your foundation if not managed properly. Tree roots can absorb moisture from the soil, causing it to shrink and shift, leading to foundation settlement.
To prevent this, maintain a safe distance between trees and your foundation. As a general rule, avoid planting trees within 20 feet of the structure. For larger trees, increase that distance accordingly. Regular pruning and trimming of trees and shrubs are also essential. Overgrown vegetation can send roots searching for moisture, potentially compromising your foundation.
3. Soil Stabilization and Compaction
The soil beneath your foundation is the literal ground upon which your home stands, so its stability is paramount. Different soil types have varying properties, and understanding how they behave is crucial in preventing foundation damage.
During construction, proper soil compaction is an absolute must. Loose or poorly compacted soil can settle over time, creating voids and spaces that allow the foundation to shift and crack. Techniques like soil amendments, which involve mixing in materials like lime or cement, can help stabilize and reinforce the soil. Retaining walls may also be necessary in some cases to prevent soil erosion and shifting around the foundation.
Once your home is built, it’s important to remain vigilant for signs of soil settlement or shifting. Cracks in the foundation walls, sticking doors or windows, or uneven floors could all be indicators of underlying soil problems that need to be addressed promptly. Regular inspections and taking action at the first signs of trouble can save you from costly and extensive foundation repairs down the line.
4. Waterproofing and Moisture Control
Even with proper drainage, moisture can still find its way into your home’s foundation through cracks, joints, or porous materials. That’s where waterproofing comes into play. There are various waterproofing methods available, including membranes, coatings, and sealants. These products create a barrier between the foundation and moisture, preventing water intrusion and potential damage.
But waterproofing alone isn’t enough. Ensuring proper ventilation and moisture control in crawl spaces or basements is equally important. Address any sources of moisture, such as leaks, condensation, or high humidity levels. Keep in mind that maintaining proper insulation and vapor barriers can help regulate moisture levels and prevent condensation buildup.
5. Seeking Professional Help
While taking preventative measures is crucial, sometimes foundation issues can still arise. That’s when it’s time to seek professional help from foundation repair experts. Regular foundation inspections by qualified professionals can identify potential problems early on before they escalate into situations requiring foundation crack repair or more significant and costly fixes.
When choosing a contractor, do your research. Look for reputable and experienced companies with a proven track record of successful foundation repairs. Don’t be afraid to ask for references and check their credentials.
Addressing foundation issues promptly is key. The longer you wait, the more extensive and expensive the repairs may become. Consult with professionals to discuss potential reinforcement or repair options that best suit your specific situation.
Closing Thoughts
Protecting your foundation from damage is an investment in the longevity and safety of your property. By implementing these five preventative measures—proper drainage, vegetation management, soil stabilization, waterproofing, and seeking professional help when needed—you can minimize the risk of foundation issues and enjoy peace of mind for years to come.